Anxiety Tech Techidemics: Understanding the Rise of Digital Stress in a Hyper-Connected Era
Technology has changed our lives in powerful ways, but it has also created new challenges that didn’t exist a decade ago. One of the most concerning issues today is what many researchers and digital-health experts describe as anxiety tech techidemics—a fast-growing wave of technology-induced stress spreading across society. This term combines anxiety, technology, and epidemic, highlighting how deeply digital pressures are affecting people of all ages.
From constant notifications to social-media comparison, from academic pressure to staying “always available,” modern technology places both visible and invisible demands on our minds. Teens and young adults often feel this even more strongly because digital tools are part of nearly every moment of their day—school, communication, entertainment, and even identity formation.
What makes the techidemics of anxiety so significant is that it doesn’t come from one single source. Instead, it is a combination of:
- Information overload from endless content
- Social pressure created by likes, comments, and digital validation
- Rapid technology changes that make people fear falling behind
- Reduced offline interaction, leading to loneliness and overthinking
- Constant connectivity, removing the space to rest mentally
These factors form a digital environment that can create stress, lower self-esteem, disturb sleep, weaken focus, and increase emotional pressure.
But understanding this phenomenon is not just about pointing out problems. It’s about exploring why it happens, how it affects different people, and—most importantly—what practical steps can help reduce tech-related anxiety without giving up the benefits technology offers.
In this detailed guide, we will break down the concept of anxiety in tech techidemics, analyze the real causes behind rising digital stress, examine who is most vulnerable, and explore proven strategies that promote healthier, balanced, and more mindful technology use.
What Is Anxiety Tech Techidemics
The term anxiety tech techidemics is a modern concept used to explain the rapid spread of technology-driven stress across different age groups, cultures, and parts of the world. It combines three ideas:
- Anxiety — the emotional and mental tension people feel
- Tech — the digital tools and platforms shaping daily life
- Techidemics — a technology-related “epidemic” of stress that spreads quickly
Why This Term Exists
Over the past decade, technology has changed faster than humans can naturally adapt. Social media apps update weekly, new devices launch every few months, and online communication never stops. This creates a constant cycle of:
- Pressure to keep up
- Fear of missing out (FOMO)
- Overthinking due to constant comparison
- Stress from instant-response expectations
- Mental fatigue from continuous notifications
As these pressures grow, more people experience anxiety symptoms triggered or intensified by digital environments. Because this problem is expanding so quickly, experts refer to it as a techidemic — a widespread, fast-moving issue rooted in technology patterns.
The Core Components of Tech-Induced Anxiety
To understand anxiety tech techidemics, it is important to recognize its main triggers:
1. Digital Pressure on Self-Image
Platforms like Instagram, TikTok, and Snapchat often portray unrealistic standards. Even adults experience self-doubt, but teens feel this much more strongly because they are still developing identity and confidence.
This can create:
- Overanalyzing appearance
- Seeking online approval
- Feeling judged or compared
2. Information Overload & Cognitive Exhaustion
The brain is not designed to process the thousands of messages, posts, videos, and alerts it receives daily.
This leads to:
- Mental exhaustion
- Difficulty focusing
- Increased stress levels
3. Fear of Not Keeping Up With Fast Technology
Every year, newer apps, A.I. tools, and digital trends appear1. Many people fear they are “falling behind,” especially students or professionals using tech for school or work.
4. Always-On Communication
The pressure to reply instantly—texts, DMs, emails—creates a constant feeling of responsibility. Teens especially feel this socially:
“Did I reply too late?”
“Will they think I’m ignoring them?”
This can lead to worry and overthinking.
5. Reduced Real-Life Social Interaction
When people spend more time online than offline, emotional support weakens. Humans need physical interaction, eye contact, and shared experiences. Without them, feelings of loneliness and anxiety grow.
Why It’s Called a “Techidemic”
A techidemic spreads not because of a virus, but because of behavioral patterns that move quickly across society:
- More screen use → more stress
- More comparison → more insecurity
- More notifications → more overwhelm
- More dependence on tech → less time to recharge mentally
As each factor grows, anxiety spreads from individuals to entire groups — students, workplaces, families, and communities.
Why Understanding This Matters
Recognizing anxiety tech techidemics is the first step to preventing long-term issues like:
- Reduced self-confidence
- Lower focus and productivity
- Sleep problems
- Emotional burnout
- Social withdrawal
Understanding these causes helps us create healthier digital habits and use technology in a balanced, mindful way.

How Technology Is Causing a Rise in Anxiety
The rise of anxiety tech techidemics is not random. It is the direct result of how modern technology influences the human brain, thinking patterns, and daily behavior. While technology offers convenience, creativity, and connection, it also introduces psychological pressures that earlier generations never experienced. Understanding how technology increases anxiety is essential to addressing the issue effectively.
Below is a detailed breakdown of the core ways technology contributes to rising anxiety levels.
Constant Notifications and Interrupted Focus
One of the biggest drivers of digital anxiety is the nonstop flow of alerts—messages, comments, likes, reminders, emails, updates, and app pings. Modern apps are intentionally designed to keep users engaged, which increases the frequency of notifications.
Why this creates anxiety:
- The brain stays in a state of heightened alertness
- Users feel pressured to respond instantly
- Constant interruptions reduce deep focus, leading to frustration
- Feeling “behind” on messages creates mental stress
Over time, this nonstop stimulation causes the brain to feel overloaded, which is a major contributor to tech-induced anxiety.
Social Comparison and Online Validation Pressure
Social media platforms are built on “performance” — posting, receiving likes, sharing updates, and monitoring how others react. While this can be positive, it also intensifies self-judgment and self-doubt.
Why this increases anxiety:
- People compare their real life to others’ highlight reels
- Fear of not looking good enough or successful enough
- Pressure to post “perfect” photos or achievements
- Worrying about who viewed, liked, or commented
For teens and young adults, this pressure can shape self-worth, leading directly to social anxiety and emotional stress.
Information Overload & Mental Fatigue
Humans were never meant to process thousands of pieces of information in a single day. But today:
- Endless news feeds
- Viral videos
- Trending topics
- Overlapping school or work apps
- Constant updates
All bombard the brain continuously.
How this causes anxiety:
- Difficulty focusing on important tasks
- Feeling mentally “drained” or overwhelmed
- Increased worry from negative news cycles
- Confusion due to too much conflicting information
This overload is one of the most common drivers of techidemics, making people feel stressed without knowing why.
Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
Social media and instant updates create a strong psychological pressure known as FOMO — the fear of being left out of something important.
Effects on anxiety:
- Checking apps repeatedly to see what’s new
- Feeling left behind when others share achievements
- Pressure to always stay updated
- Emotional discomfort when not online
FOMO is a major factor in digital dependency, which increases anxiety when users try to disconnect.
Academic and Productivity Pressures
Technology is deeply integrated into school, work, and learning environments.
Why this causes stress:
- Pressure to meet faster deadlines
- Difficulty focusing due to multitasking
- Overthinking about grades or performance perfection
- Being expected to always “keep up” with new tools
Teens and students often feel overwhelmed trying to balance apps, online classes, study resources, deadlines, and social media simultaneously.
Reduced Real-World Interaction
Even though technology connects people digitally, it often decreases face-to-face communication — which is essential for emotional well-being.
How this leads to anxiety:
- Feeling lonely despite being “connected”
- Misinterpreting digital messages and overthinking
- Decreased ability to express thoughts in person
- Loss of real emotional support
Loneliness and isolation are major contributors to the spread of anxiety tech techidemics.
Sleep Disruption from Late-Night Screen Time
Blue light from screens signals the brain to stay awake. Combined with late-night scrolling or chatting, this disrupts sleep patterns.
Impact:
- Trouble falling asleep
- Waking up tired
- Poor emotional regulation
- Increased stress and irritability
Poor sleep is one of the strongest predictors of anxiety.
Rapid Technological Change & Fear of Falling Behind
New trends, apps, tools, and tech skills appear constantly.
This creates anxiety because:
- People feel pressure to stay updated
- Fear of being “outdated” or less capable
- Stress about missing new opportunities
- Confusion from constant change
This is especially strong in students, creators, and professionals who rely on digital tools.
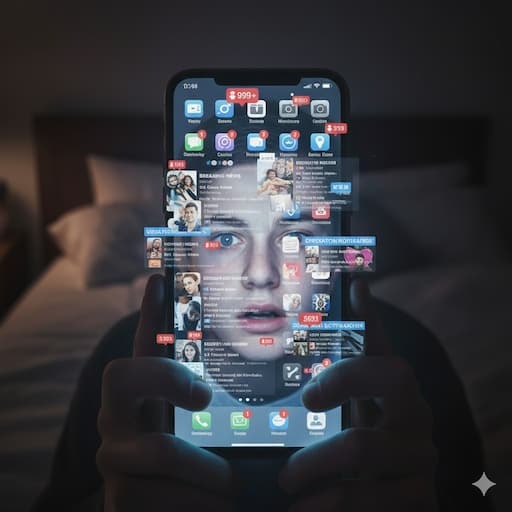
Who Is Most Affected by Anxiety Tech Techidemics?
The impact of anxiety tech techidemics is not the same for everyone. Different groups experience tech-induced stress for different reasons—some due to emotional development, others because of academic pressure, workplace demands, or social expectations. Understanding who is most vulnerable helps reveal why this issue is spreading so quickly and how it affects society at multiple levels.
Below is a complete, in-depth examination of the groups most affected.
Teenagers (13–19 Years) — The Most Vulnerable Group
Teens are at the center of the techidemics wave because digital technology is deeply woven into their identity, social life, and learning environment.
🔹 Why teens are most affected:
- They experience high social-comparison pressure
- Their self-esteem is still developing
- Peer approval matters more at this age
- They rely heavily on phones for communication
- Academic and social life both happen online
🔹 Types of anxiety teens face:
- Fear of missing out (FOMO)
- Worry about likes, comments, and appearance
- Anxiety about fitting in socially
- Fear of judgment or bullying online
- Stress from juggling school apps, assignments, and notifications
Because teens spend the most time online, they often feel the strongest emotional impact.
Students (High School & University)
Students face academic pressure on top of social pressure. Technology is essential for studies, but the overload can easily become overwhelming.
Why students are affected:
- Online classes, homework portals, digital submissions
- High expectation to stay updated with tech tools
- Competitive academic environments
- Social pressure from peers online
- Lack of real-life interaction due to heavy screen usage
Types of anxiety:
- Study-related tech stress
- Difficulty focusing due to multitasking
- Fear of falling behind academically
- Overthinking due to academic comparisons
Students often experience “double anxiety”: academic + digital.
Young Adults (20–30 Years)
Young adults are entering careers or building independence, which makes technology both necessary and stressful.
Why young adults are affected:
- Pressure to build a perfect online image
- Career-related fear of missing opportunities
- Competition in digital workplaces
- Job applications, skill-learning, and networking all happen online
- Financial stress amplified by comparison with peers
Common anxiety triggers:
- Professional social media pressure (LinkedIn, personal branding)
- Fear of not mastering new tech tools
- Comparison to friends’ achievements
- Overthinking due to hyper-productivity culture
This age group often struggles with “achievement anxiety” amplified by technology.
Working Professionals
Workplaces depend heavily on fast-changing technologies—emails, project apps, online meetings, A.I. tools—making many professionals feel constantly overwhelmed.
What professionals struggle with:
- Rapid response expectations
- Heavy multitasking
- Meeting overload
- Constant updates and software changes
- Pressure to stay online even after work hours
Emotional effects:
- Burnout
- Low motivation
- Stress from tight deadlines
- Anxiety about job performance
Professionals often face “tech burnout,” a major part of the techidemics wave.
Content Creators & Social Media Influencers
Creators depend on online visibility, which puts intense psychological pressure on their mental health.
Why they’re affected:
- Pressure to post regularly
- Algorithm changes affecting reach
- Fear of losing followers
- Negative comments and criticism
- Need to constantly stay “relevant”
This group experiences high-performance stress that fuels anxiety tech techidemics.
Parents & Guardians
Parents struggle not only with their own tech stress but also with managing their children’s online habits.
Why parents experience anxiety:
- Fear for children’s safety online
- Concern about screen addiction
- Pressure to monitor multiple platforms
- Worry about cyberbullying or negative influences
- Difficulty balancing tech rules at home
Parents often feel emotionally overloaded trying to protect their kids from digital risks.
Older Adults & Late Adopters
Adults who didn’t grow up with modern technology often feel pressured to adapt quickly.
Causes of anxiety:
- Confusion with new apps or devices
- Fear of “falling behind” younger generations
- Pressure to use digital payments, online services, etc.
- Struggles with fast-changing updates
This is known as technology-adaptation anxiety, a growing part of techidemics.
People With Pre-Existing Anxiety or Mental Health Challenges
For those already struggling with emotional health, technology can intensify symptoms.
Why:
- Overthinking is triggered easily
- Online negativity feels heavier
- Social pressure increases sensitivity
- Sleep disruption worsens anxiety
- Harder to disconnect and recharge
This group requires extra support and healthier digital routines.
What Is Anxiety Tech in the Era of Techidemics?
In today’s digital era, the term anxiety tech has become central to discussions about mental health, especially within the growing phenomenon known as techidemics. Techidemics refers to the widespread, fast-spreading influence of modern technology on human behavior, emotions, decision-making, and overall well-being. As digital tools become deeply embedded in daily life, they can generate convenience and innovation—yet they also contribute to psychological strain, worry, and overstimulation.
Anxiety tech describes the increasing stress and pressure created directly or indirectly by digital devices, algorithms, online systems, and emerging technologies. It includes the mental load people face due to constant notifications, social comparison on social media, fear of falling behind in a rapidly changing tech world, privacy concerns, digital skills pressure, and overwhelming information flow.
Why Anxiety Tech Has Become a Serious Issue Today
The rise of anxiety tech is not accidental—it’s the outcome of how modern technology has evolved. We now live in a world where:
- Your phone demands attention dozens to hundreds of times a day.
- Social media algorithms push content designed to intensify emotional reactions.
- AI tools change how we learn, work, and socialize, making many feel uncertain or unprepared.
- The digital world operates 24/7, leaving little room for mental rest.
- Students and professionals feel they must constantly stay updated or risk falling behind.
These factors fuel what experts call a techidemic — a digital epidemic affecting emotional stability on a global scale.
How Anxiety Tech Impacts Teens, Adults, and Professionals
Different groups experience anxiety tech differently:
- Teens may feel pressure to always look perfect online or maintain constant digital presence.
- Students experience academic stress due to online competition, productivity tools, and AI-driven academic systems.
- Professionals feel overwhelmed by the fast pace of technological change, automation fears, constant emails, and remote work expectations.
- Parents worry about screen exposure, online safety, and their children’s digital habits.
Regardless of age, almost everyone now faces some form of digital stress—making anxiety tech one of the defining mental-health challenges of modern life.
Why Techidemics Makes Anxiety Tech Worse
The concept of techidemics highlights how technology spreads its effects rapidly, similar to how epidemics spread.
This means:
- One technological change can affect millions instantly.
- Stress and overwhelm spread across communities faster than ever.
- People compare themselves online, increasing emotional pressure.
- Digital problems—like misinformation, cyberbullying, or privacy fears—spread at a massive scale.
As a result, anxiety tech is not limited to individuals—it’s a global psychological shift.
How Technology Triggers Stress, Overthinking, and Digital Overload
The rapid rise of digital tools has dramatically reshaped how people think, communicate, and manage daily life. While technology brings convenience, entertainment, and innovation, it also creates new forms of psychological pressure. This modern stress—often referred to as anxiety tech—is a core driver behind the growing global techidemics.
In this section, we explore exactly how technology triggers anxiety, why it feels overwhelming, and how constant digital exposure can rewire thinking patterns.
Information Overload and Mental Fatigue
We are exposed to more information in a single day than previous generations consumed in weeks. This constant stream of news, messages, alerts, updates, and social feeds overstimulates the brain.
Why it creates anxiety
- The brain is not designed for unlimited input.
- Constant content consumption forces your mind into a never-ending data-processing mode.
- Mental fatigue leads to stress, reduced focus, and emotional imbalance.
- You begin to feel pressure to keep up, even when it’s impossible.
What this looks like in real life
- Switching between apps every few minutes
- Feeling tired even after resting
- Difficulty making decisions because of too much information
- Feeling overwhelmed by the pressure to stay updated
This cycle fuels the techidemics because it affects millions simultaneously.
Constant Notifications and Interrupted Focus
Every ping, vibration, or alert forces your brain to switch tasks. Even small notifications can break focus for up to 20–25 minutes, according to cognitive research.
How notifications become anxiety tech
- They create a sense of urgency
- They force your attention away from important tasks
- They produce micro-stress every time they interrupt your thoughts
- They make your brain expect constant stimulation
Over time, this leads to irritability, impatience, and restlessness—key signals of technology-driven anxiety.
Social Media Comparison and Emotional Pressure
Social platforms are designed to highlight the best moments, achievements, and filtered lifestyles of others. This creates unrealistic expectations and emotional pressure.
Impact on the mind
- Feelings of not being good enough
- Fear of missing out (FOMO)
- Worrying about likes, comments, and engagement
- Stress from maintaining an online image
This psychological effect spreads rapidly in a techidemic-like pattern, especially among teens and young adults.
Fear of Falling Behind in a Fast Tech World
AI, automation, digital skills, and new apps evolve daily. Many people—whether students or professionals—feel they cannot keep up.
This leads to:
- Performance stress
- Overthinking future job security
- Pressure to learn everything instantly
- Anxiety about being replaced by technology
This fear becomes a major part of anxiety tech, especially in competitive environments.
Digital Workplace Stress & Remote Work Pressure
Technology has blurred the line between personal life and work/school life2.
Common stress triggers
- Always being expected to respond
- Emails and messages at all hours
- Multiple online platforms to manage tasks3
- Video-call fatigue
- Monitoring tools that increase pressure
This creates a high-stress digital lifestyle that contributes to worldwide techidemics.
The Hidden Stress of Privacy and Security Concerns
Many users constantly worry about:
- Data leaks
- Tracking
- Scams
- AI misuse
- Online identity and safety
Even if nothing goes wrong, the fear itself becomes a form of anxiety tech.

The Rise of Techidemics: Why Digital Anxiety Is Spreading Globally
As digital technology becomes an inseparable part of daily life, anxiety in tech techidemics is no longer a niche concern—it’s a global phenomenon. The term techidemics captures how anxiety linked to technology spreads rapidly across societies, age groups, and communities, much like a digital epidemic. This section explores why tech-induced anxiety is growing worldwide and what factors accelerate its spread.
Global Increase in Screen Time
Screen time has surged exponentially in the last decade:
- Smartphones, tablets, and computers are used for school, work, and entertainment
- Social media apps dominate hours of daily attention
- Streaming, gaming, and online learning increase exposure
Impact on anxiety
- Constant screen exposure overstimulates the brain
- Lack of offline downtime prevents mental recovery
- Higher screen time correlates with increased stress and sleep disruption
Statistics: Studies show that teens spend an average of 7–9 hours per day on screens outside schoolwork, contributing significantly to tech-induced stress.
Social Media as a Stress Multiplier
Social platforms amplify emotional pressure:
- Comparison with peers increases self-doubt
- Fear of missing out (FOMO) fuels constant checking
- Online harassment, cyberbullying, or negative comments exacerbate anxiety4
Because these platforms are global, anxiety spreads quickly across networks, creating a shared techidemic experience.
Rapid Technological Change
Technology evolves faster than individuals can adapt:
- AI, automation, and new apps emerge continuously
- Job, learning, and social demands shift rapidly
- Individuals feel a constant pressure to stay updated
Effect on mental health
- Fear of falling behind professionally or academically
- Overthinking and mental fatigue from trying to keep pace
- Stress about future uncertainty
The faster the tech evolves, the stronger the techidemic effect.
Global Connectivity and Digital Culture
Digital connectivity allows trends, challenges, and behaviors to spread instantly:
- Viral social media challenges
- Online “comparison culture”
- Digital norms for behavior, productivity, and success
This global culture accelerates the spread of anxiety tech, making it a worldwide issue rather than isolated incidents.
Workplace and Educational Pressures in a Digital Era
- Remote work and online learning blur boundaries between personal and professional life
- Employees and students are expected to respond quickly, stay productive, and adapt to new tools
- “Always-on” digital expectations create chronic stress
These pressures create anxiety in millions of people, contributing to a techidemic effect across organizations and countries.
COVID-19 and Accelerated Digital Dependence
The pandemic dramatically increased reliance on technology:
- Remote learning and work became mandatory
- Social interactions shifted online
- Screen fatigue, online stress, and digital burnout increased
Even as the world returns to in-person activities, digital habits remain, sustaining the techidemic globally.
Summary: Why Anxiety Tech Techidemics Are Spreading
In short, the global rise of anxiety tech is driven by:
- More screen time → overstimulation and fatigue
- Social media pressure → constant comparison and FOMO
- Rapid technological change → fear of falling behind
- Global digital culture → stress spreads quickly
- Digital work & study demands → blurred boundaries
- Pandemic-driven digital dependence → long-term habit formation
Signs, Symptoms, and Effects of Anxiety Tech Techidemics
As anxiety tech techidemics continues to rise, it becomes increasingly important to recognize the physical, emotional, and behavioral signs of digital-induced stress. Early recognition allows individuals to manage tech-related anxiety effectively before it affects long-term mental and physical health.
Emotional and Psychological Symptoms
Anxiety caused by excessive technology use often manifests in emotional and mental patterns, such as:
- Constant worry or overthinking about messages, notifications, or online reputation
- Restlessness and inability to relax without a digital device
- Irritability or mood swings when unable to access devices
- Feeling overwhelmed by constant information or updates
- Low self-esteem due to social comparison or online judgment
These symptoms can appear subtly at first but intensify with prolonged tech dependence.
Behavioral Symptoms
Technology-induced anxiety can also lead to observable behavioral changes, including:
- Checking devices compulsively—even during meals, study sessions, or meetings
- Difficulty focusing on offline tasks due to mental distraction
- Avoiding social interactions in favor of online engagement
- Procrastination or multitasking excessively with multiple apps and notifications
- Over-preparation or perfectionism in online posts or content
Behavioral patterns like these indicate that tech has begun to dominate attention and decision-making, a hallmark of techidemics.
Physical Symptoms
Prolonged exposure to technology combined with anxiety triggers physical responses, such as:
- Sleep disturbances (difficulty falling asleep, poor quality of sleep, late-night scrolling)
- Headaches or eye strain from extended screen time
- Muscle tension and posture problems due to device use
- Fatigue and low energy from overstimulation and poor rest
- Digestive or stress-related issues from chronic anxiety
The combination of mental and physical stress reinforces tech-driven anxiety.
Cognitive and Productivity Effects
Technology can impact thinking and productivity, further fueling anxiety tech:
- Reduced attention span and inability to focus on one task for long
- Decision fatigue from constant online choices and notifications
- Difficulty processing information due to information overload
- Memory lapses or forgetting offline responsibilities due to multitasking online
These cognitive effects create a feedback loop—reduced productivity leads to more stress, and stress leads to more compulsive tech use.
Social and Relationship Effects
Anxiety tech techidemics also affects social well-being:
- Reduced face-to-face interactions
- Miscommunication or over-analyzing online messages
- Feelings of isolation despite being “connected” digitally
- Conflict with family, friends, or colleagues over screen habits
- Difficulty maintaining long-term relationships due to divided attention
Digital anxiety can subtly erode social bonds if not addressed.
Early vs. Advanced Signs
- Early signs: mild restlessness, checking phone frequently, small sleep disruptions, occasional worry about online image
- Advanced signs: chronic stress, severe insomnia, mood swings, social withdrawal, burnout, persistent low self-esteem
Recognizing early warning signs allows individuals to take action before techidemics significantly impact mental health.
Effective Strategies to Reduce Anxiety Tech Techidemics
While technology is an integral part of modern life, it is possible to manage anxiety and tech techidemics through mindful practices, healthier digital habits, and strategic interventions. This section explores proven strategies to reduce tech-induced stress and restore balance.
Set Boundaries for Screen Time
- Schedule device-free periods: Allocate specific times for offline activities, such as meals, exercise, or reading.
- Use app timers: Many devices have built-in screen-time tracking and limits.
- Prioritize offline tasks: Focus on real-life responsibilities first, reducing the pressure of digital distractions.
✅ Benefits:
- Reduces overstimulation
- Improves focus and productivity
- Promotes mental recovery
Practice Mindful Technology Use
Mindfulness is about being present in the moment, even when using technology.
- Limit multitasking between apps
- Focus on one task at a time
- Pay attention to emotions triggered by digital content
- Reflect on why you are using a device (habit vs. intentional use)
✅ Benefits:
- Reduces anxiety from compulsive checking
- Enhances self-awareness
- Improves emotional regulation
Manage Social Media Pressure
- Curate your feeds: Unfollow accounts that trigger comparison or stress
- Limit scrolling time: Use apps to set time caps on social media
- Take regular social media breaks: Digital detox for 1–3 days can reset mental load
- Focus on positive engagement: Interact with supportive communities rather than stressful content
✅ Benefits:
- Reduces FOMO
- Protects self-esteem
- Encourages healthier online interactions
Improve Sleep Hygiene
- Avoid screens at least 30–60 minutes before bed
- Use blue-light filters if screen use is unavoidable
- Maintain a consistent sleep schedule
- Use relaxation techniques like deep breathing or meditation
✅ Benefits:
- Better emotional regulation
- Less fatigue and irritability
- Reduced chronic stress
Strengthen Offline Relationships
- Spend quality time with family and friends without devices
- Engage in face-to-face conversations
- Participate in group activities, sports, or hobbies
- Balance online and offline communication
✅ Benefits:
- Increases emotional support
- Reduces feelings of loneliness
- Enhances social skills and well-being
Develop Healthy Coping Skills
- Journaling to track emotions and stress triggers
- Breathing exercises or meditation apps
- Physical activity to reduce tension
- Limiting multitasking to reduce cognitive overload
✅ Benefits:
- Lowers mental tension
- Builds resilience against tech-induced stress
- Provides tools for managing digital anxiety
Educate About Technology Use
- Learn how apps and social platforms influence emotions
- Discuss digital stress with peers, parents, or teachers
- Stay informed about digital wellness strategies
✅ Benefits:
- Promotes informed and intentional tech use
- Reduces anxiety through understanding
- Empowers individuals to make conscious decisions
Seek Professional Help if Needed
- Therapists or counselors can provide guidance on digital anxiety
- Cognitive-behavioral techniques are effective for tech-induced stress
- Support groups can provide shared strategies and experiences
✅ Benefits:
- Provides professional coping strategies
- Reduces chronic anxiety
- Helps restore mental and emotional balance
Future Outlook: How Technology and Mental Health Can Coexist
While anxiety tech techidemics is a growing concern, the future of technology does not have to mean rising stress and digital burnout. With intentional design, digital literacy, and mindful usage, technology can coexist with good mental health and even support emotional well-being.
The Role of Tech Companies in Reducing Anxiety
Tech developers are beginning to recognize the mental-health impact of their platforms:
- Mindful app design: Reducing notification overload and addictive features
- Digital wellness tools: Built-in screen-time trackers, focus modes, and reminders for breaks
- AI-powered support: Personalized mental-health tips and stress detection features
- Transparency in algorithms: Helping users understand why certain content appears
✅ Future Benefit:
Users can engage with technology without falling into compulsive habits, reducing the spread of techidemics.
Digital Literacy and Education
Teaching digital literacy can empower individuals to manage anxiety tech effectively:
- Understanding online influence on emotions
- Recognizing signs of digital stress
- Learning safe and intentional online behavior
- Promoting responsible device usage from a young age
✅ Future Benefit:
Educated users are more aware of their habits and better equipped to prevent tech-induced anxiety.
Integrating Mindfulness and Technology
Future trends may focus on mindful technology—tools that support well-being rather than just engagement:
- Meditation apps that encourage real breaks
- Focus apps that promote offline productivity
- AI reminders for healthy digital habits
- Platforms that prioritize positive interactions and mental health over clicks
✅ Future Benefit:
Technology becomes a partner for mental health rather than a source of stress.
Hybrid Models of Digital and Offline Life
The key to reducing techidemics lies in balance:
- Structured online time combined with offline activities
- Tech-assisted learning or work without constant connectivity5
- Encouraging social interaction in real life alongside digital networking
✅ Future Benefit:
Individuals maintain productivity and creativity while protecting mental health, reducing long-term anxiety trends.
Policy and Public Awareness Initiatives
Governments and organizations may implement policies to address digital stress:
- Public campaigns on digital wellness
- Guidelines for healthy screen usage in schools and workplaces
- Regulations to minimize harmful online content and cyberbullying
✅ Future Benefit:
A societal-level approach can reduce tech-induced stress across populations, curbing the spread of techidemics.
The Vision Ahead
The future does not need to be dominated by anxiety tech. By combining:
- User education
- Conscious tech design
- Mindful usage practices
- Supportive policies
…technology can support mental health instead of harming it. With awareness and proactive steps, anxiety tech techidemics can be mitigated while still enjoying the benefits of innovation and connectivity.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is anxiety tech techidemics?
Anxiety tech techidemics refers to the widespread increase in anxiety and stress caused by modern technology. It combines the concepts of anxiety, technology, and epidemic, highlighting how digital pressure—from constant notifications, social media comparison, and information overload—is affecting people globally. It’s a mental-health phenomenon where technology-driven stress spreads quickly across different age groups and communities.
Who is most affected by anxiety tech techidemics?
While anyone can experience technology-induced stress, certain groups are more vulnerable:
- Teens and young adults: High social comparison and identity formation pressures.
- Students: Academic stress and multitasking across online platforms.
- Professionals: Workplace pressures, remote work, and constant connectivity.
- Parents: Managing children’s screen time and digital safety.
- Older adults or late tech adopters: Difficulty adapting to rapid tech changes.
What are the common signs and symptoms?
Anxiety tech techidemics can manifest in emotional, behavioral, physical, and cognitive ways:
- Emotional: Constant worry, irritability, mood swings, low self-esteem
- Behavioral: Compulsive device checking, multitasking, social withdrawal
- Physical: Sleep disruption, headaches, eye strain, fatigue
- Cognitive: Reduced focus, decision fatigue, memory lapses
Recognizing these signs early can help prevent long-term mental health problems.
How can I reduce tech-induced anxiety?
Effective strategies include:
- Setting screen-time boundaries and offline breaks
- Practicing mindfulness while using technology
- Curating social media to reduce comparison and FOMO
- Improving sleep hygiene and reducing late-night device use
- Strengthening offline relationships and social support
- Developing coping skills like journaling, exercise, or meditation
- Seeking professional help if anxiety becomes chronic
Can technology ever help reduce anxiety?
Yes. While technology can cause anxiety, it can also help manage it if used intentionally. Digital wellness apps, meditation apps, screen-time trackers, AI-driven mental-health tools, and online support communities can all support better mental health. The key is mindful, balanced, and informed use rather than constant, compulsive engagement.
Is anxiety tech techidemics a temporary trend or a long-term issue?
Anxiety about tech techidemics is a long-term concern because technology continues to evolve rapidly, and digital connectivity is becoming essential in education, work, and social life. However, with proper awareness, digital literacy, and mindful habits, its effects can be managed, reducing stress and preventing widespread chronic anxiety.
Conclusion
The rise of anxiety tech techidemics highlights one of the most pressing mental-health challenges of the digital era. Technology has revolutionized how we learn, work, and connect, but it also introduces stress, overthinking, and emotional overload that affect millions worldwide. From teens and students to professionals and parents, no age group is completely immune.
Through this article, we’ve explored:
- What anxiety tech techidemics is: the intersection of technology, anxiety, and rapid societal spread
- How technology triggers stress: constant notifications, social comparison, information overload, and FOMO
- Who is most affected: teens, students, young adults, professionals, and even parents
- Signs and symptoms: emotional, behavioral, cognitive, and physical effects
- Practical strategies: mindfulness, screen-time management, social media moderation, sleep hygiene, offline engagement, and professional support
- Future outlook: how technology can coexist with mental health through mindful design, digital literacy, and balanced usage
See More:
References
- “Social media use, mental health and sleep: A systematic review with meta-analyses.” PubMed / Elsevier, 2024. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39242043/ PubMed ↩︎
- “The Digital Dilemma: Patterns of Screen Time, Sleep Quality, and Mental Health Among Saudi University Students.” PMC / PubMed, (Saudi Arabia study). https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC12510793/ PubMed Central+1 ↩︎
- Xu, Duan, Qin & Liu. “Association between screen time and depressive and anxiety symptoms among Chinese adolescents.” PubMed, 2025. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/40395468/ PubMed ↩︎
- Adanyin, Anthonette. “AI‑Driven Feedback Loops in Digital Technologies: Psychological Impacts on User Behaviour and Well‑Being.” arXiv preprint, 2024. https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.09706 ↩︎
- Wanger, Jessica. “Is technology creating an anxious generation?” World Economic Forum, 2024. https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2024/05/technology-creating-an-anxious-generation/ World Economic Forum ↩︎

