Cancer: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Latest Treatments
Cancer is a serious disease that occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably and spread to other parts of the body. It is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, with millions of new cases reported every year.
The most common types of cancer include breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, and skin cancer. Early cancer detection through regular screening tests plays a vital role in improving survival rates.
Understanding cancer symptoms such as unexplained weight loss, persistent fatigue, or unusual lumps can help with timely diagnosis.
Modern cancer treatments such as chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and immunotherapy have improved patient outcomes significantly.
Ongoing cancer research continues to find new ways to prevent, detect, and cure this life-threatening disease.
Types of Cancer
- Breast Cancer
- Cancer that forms in breast tissue, most common in women but can also occur in men.
- Lung Cancer
- Affects the lungs, often linked to smoking or exposure to harmful substances.
- Prostate Cancer
- Develops in the prostate gland of men; common in older men.
- Skin Cancer
- Includes melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma; caused by UV exposure.
- Colon & Rectal Cancer (Colorectal Cancer)
- Cancer of the colon or rectum; early detection through screening is vital.
- Cervical Cancer
- Cancer of the cervix, often linked to HPV infection, is preventable with vaccination and regular Pap tests.
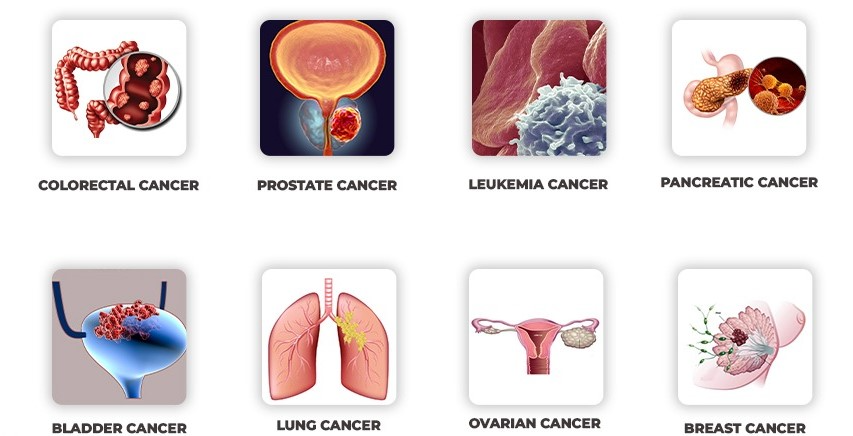
- Leukemia (Blood Cancer)
- Cancer of the blood or bone marrow affects white blood cells and immune function.
- Lymphoma
- Cancer of the lymphatic system; includes Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma.
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Cancer in the pancreas; often detected at an advanced stage, making it aggressive.
- Brain Cancer
- Cancer that starts in or spreads to the brain; it may cause neurological symptoms like headaches and seizures.
- Ovarian Cancer
- Affects the ovaries in women; often detected late due to subtle early symptoms.
- Stomach (Gastric) Cancer
- Cancer of the stomach lining; associated with diet, infections, and genetics.
How Common is Cancer? Key Statistics and Facts
Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. According to global data:
- Over 19 million new cancer cases are diagnosed annually (2024 statistics).
- More than 10 million deaths occur from cancer each year.
- The most common types of cancer include breast cancer, lung cancer, prostate cancer, and colorectal cancer.
- The risk of developing cancer increases with age, but lifestyle factors, genetics, and environmental exposures also play a significant role.
- Early cancer detection and screening significantly improve survival rates, highlighting the importance of awareness about cancer symptoms and risk factors.
Cancer Causes Explained: Genetics, Lifestyle, and Environmental Factors
Cancer is a complex disease that occurs when abnormal cells grow uncontrollably. Understanding the causes of cancer is essential for prevention and early detection.
Several factors contribute to the development of cancer:
- Genetic Factors and Family History:
Inherited gene mutations can increase the risk of cancers such as breast cancer, ovarian cancer, and colon cancer. A family history of cancer makes regular screening tests even more important. - Unhealthy Lifestyle Choices:
Poor diet, lack of physical activity, smoking, and excessive alcohol consumption are major cancer risk factors. Making healthy lifestyle changes can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing cancer. - Environmental Exposures:
Long-term exposure to radiation, chemicals, pesticides, and air pollution can trigger cancer. Workplace safety and avoiding harmful substances play a key role in cancer prevention.
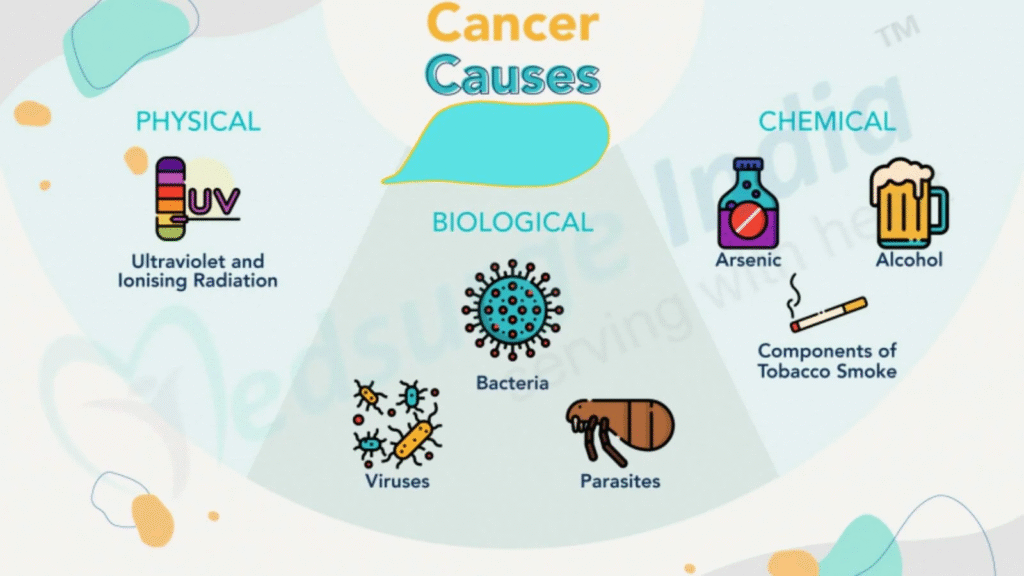
Infections Linked to Cancer:
Certain infections caused by HPV, Hepatitis B and C, and Helicobacter pylori are associated with cancers such as cervical cancer, liver cancer, and stomach cancer. Vaccinations and proper hygiene can help lower this risk.
- Hormonal and Age-Related Factors:
Hormonal imbalances and aging increase the risk of cancers like breast cancer and prostate cancer, as cells accumulate damage over time. - Weakened Immune System:
A compromised immune system may fail to detect and destroy abnormal cells, allowing cancer to develop and progress.
Symptoms of Cancer: Early Warning Signs You Should Know
Recognizing cancer symptoms early can save lives. While symptoms vary depending on the type of cancer, some common warning signs include:
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Sudden weight loss without changes in diet or exercise may indicate cancer, such as pancreatic, stomach, or lung cancer.
- Persistent Fatigue
- Feeling extremely tired, even after rest, can be an early symptom of blood cancer (leukemia), colon cancer, or breast cancer.
- Unusual Lumps or Swelling
- Lumps in the breast, neck, or underarm could be a sign of breast cancer, lymph node cancer, or soft tissue tumors.
- Changes in Skin
- Skin cancer may present as new moles, dark spots, sores that don’t heal, or changes in existing moles.
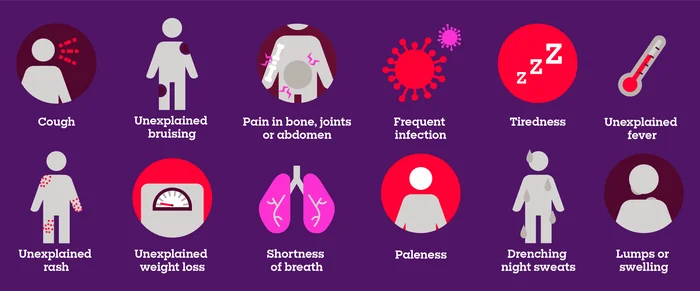
- Persistent Pain
- Ongoing pain in the bones, joints, or abdomen can indicate certain cancers like bone, ovarian, or pancreatic cancer.
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Habits
- Colon, bladder, or prostate cancer may cause diarrhea, constipation, blood in stool, or frequent urination.
- Unexplained Bleeding or Bruising
- Blood in urine, stool, or unusual bruising can be a warning sign of blood cancer, colon cancer, or cervical cancer.
- Difficulty Swallowing or Persistent Cough
- May indicate lung, throat, or esophageal cancer.
- Fever or Infections
- Frequent infections or prolonged fever can signal blood cancer or weakened immunity due to cancer.
Complications of Cancer: Risks and Health Challenges
Cancer can lead to numerous complications that affect both physical health and quality of life. Understanding these complications helps patients, caregivers, and healthcare providers manage the disease more effectively.
1. Metastasis (Cancer Spread)
- Cancer cells can spread to other organs, such as the liver, lungs, or brain, creating secondary tumors.
- Metastatic cancer is harder to treat and may reduce survival rates.
2. Organ Damage and Failure
- Tumors can impair vital organs like the lungs, liver, kidneys, and heart, leading to severe health problems.
3. Chronic Pain and Discomfort
- Advanced cancers may cause persistent pain, swelling, or nerve damage, requiring pain management and palliative care.
4. Fatigue and Weakness
- Cancer-related fatigue is common due to the disease itself or treatments such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
- It can lead to reduced mobility and affect daily activities.
5. Immune System Suppression
- Some cancers, especially blood cancers like leukemia and lymphoma, weaken the immune system, increasing susceptibility to infections.
6. Emotional and Mental Health Issues
- Patients may experience anxiety, depression, and stress, impacting recovery and overall well-being.
7. Treatment-Related Complications
- Chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery can cause side effects such as nausea, hair loss, skin changes, organ toxicity, and anemia.
How Is Cancer Diagnosed? Methods & Statistics
Accurate and timely cancer diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment and improved survival rates.
While screening tests play a role, the majority of cancers are diagnosed through clinical evaluation and diagnostic procedures.
Diagnostic Methods
- Physical Examination – Checking for lumps, skin changes, or swelling.
- Imaging Tests – Techniques like X-rays, CT scans, and MRI scans help detect tumors. Modern imaging technologies such as MRI play a vital role in early cancer detection — learn more about imaging careers in how to become an MRI tech.
- Laboratory Tests – Blood and urine tests reveal tumor markers or abnormalities.
- Biopsy – Tissue samples examined microscopically to confirm cancer.
- Endoscopic Procedures – Colonoscopy and bronchoscopy allow direct visualization of internal organs.
- Genetic and Molecular Testing – Identifies specific gene mutations for personalized treatment.
- Genetic and Molecular Testing
- Tests identify specific gene mutations or biomarkers, guiding personalized treatment plans.
Cancer Diagnosis Statistics
- Incidence: In the United States, approximately 1.85 million new cancer cases were reported in 2022.
- Screening Limitations: Only about 14% of cancers are detected through recommended screening tests. The majority are identified when symptoms appear or during other medical care.
- AI in Diagnosis: Recent advancements in artificial intelligence have shown promise in improving early cancer detection, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Cancer Management and Treatment: Comprehensive Guide
Effective cancer management involves a combination of treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and supportive care tailored to the patient’s type and stage of cancer. Healthcare facilities increasingly rely on workforce management software to coordinate oncology staff and streamline patient care.
1. Surgery
- Surgical procedures aim to remove tumors or affected tissues.
- Commonly used for breast cancer, colon cancer, and skin cancer.
- Sometimes combined with chemotherapy or radiation therapy for better outcomes.
2. Chemotherapy
- Cancer-fighting drugs target rapidly dividing cells.
- Can be administered orally, intravenously, or regionally.
- Side effects may include nausea, hair loss, and fatigue.
3. Radiation Therapy
- Uses high-energy radiation to destroy cancer cells.
- Effective for brain cancer, lung cancer, and prostate cancer.
- Often combined with surgery or chemotherapy.
4. Immunotherapy
- Boosts the immune system to attack cancer cells.
- Used for cancers like melanoma, lung cancer, and certain blood cancers.
- Includes checkpoint inhibitors and CAR-T cell therapy.
5. Targeted Therapy
- Drugs focus on specific genes, proteins, or pathways involved in cancer growth.
- Minimizes damage to healthy cells compared to traditional chemotherapy.
6. Hormone Therapy
- Blocks hormones that fuel cancer growth, used in breast cancer and prostate cancer.
7. Supportive and Palliative Care
- Focuses on relieving pain, managing symptoms, and improving quality of life.
- Includes nutrition management, psychological support, and rehabilitation.
8. Lifestyle Management in Cancer Care
- Maintaining a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress reduction helps improve treatment outcomes.
- Avoiding smoking, alcohol, and exposure to carcinogens is crucial in cancer management.
Recent Advances in Cancer Treatment
Precision medicine and genetic testing allow for personalized treatment plans. AI-assisted diagnostics help identify optimal therapies and improve survival rates. Research and innovation in technology-driven education, such as programs offered at Wentworth Institute of Technology, contribute to advances in healthcare diagnostics and treatment.
Ongoing clinical trials continue to expand future cancer therapies.
Cancer Prevention: Evidence-Based Strategies to Lower Risk
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing various cancers.
Maintaining overall health and managing chronic diseases such as high blood pressure can also reduce cancer risks.
According to the American Cancer Society, in 2024, the United States is projected to have over 2 million new cancer cases and approximately 611,720 cancer deaths.
Implementing preventive strategies can help lower these numbers.
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Obesity is linked to an increased risk of several cancers, including breast, liver, kidney, and colorectal cancers.
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can reduce cancer risk and improve overall health.
2. Engage in Regular Physical Activity
- Regular exercise helps maintain a healthy weight and may lower the risk of cancers such as breast and colon cancer.
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise per week.
3. Adopt a Healthy Diet
- Emphasize a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes.
- Limit consumption of processed foods, red meats, and sugary beverages.
- The World Cancer Research Fund recommends consuming at least 30 grams of fiber per day and at least 400 grams (5 servings) of fruits and vegetables daily.
4. Avoid Tobacco Products
- Smoking is a leading cause of lung, throat, mouth, and bladder cancers.
- Quitting smoking and avoiding exposure to secondhand smoke can significantly reduce cancer risk.
5. Limit Alcohol Consumption
- Excessive alcohol intake is associated with an increased risk of cancers such as liver, breast, and esophageal cancers.
- Limiting alcohol consumption can lower these risks.
6. Protect Skin from the Sun
- Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can increase the risk of skin cancers, including melanoma.
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30, wear protective clothing, and avoid tanning beds.
7. Get Vaccinated
- Vaccines can protect against certain cancer-causing infections:
- The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine is used to prevent cervical and other cancers.
- The Hepatitis B vaccine reduces the risk of liver cancer.
- The human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccine is used to prevent cervical and other cancers.

8. Participate in Regular Screenings
- Early detection through screenings can identify cancers at an early, more treatable stage:
- Mammograms for breast cancer.
- Pap smears and HPV tests for cervical cancer.
- Colonoscopy for colorectal cancer.
- Lung cancer screening for high-risk individuals.
- Mammograms for breast cancer.
9. Avoid Exposure to Environmental Carcinogens
- Limit exposure to known carcinogens such as asbestos, radon, and certain chemicals in the workplace.
- Follow safety guidelines and use protective equipment when necessary.
10. Consider Chemoprevention for High-Risk Individuals
- For individuals at high risk of certain cancers, medications may help reduce risk:
- Aspirin for colorectal cancer prevention in some individuals.
- Tamoxifen or raloxifene for breast cancer prevention in high-risk women.
- Aspirin for colorectal cancer prevention in some individuals.
FAQ’s:
What is cancer?
Cancer is a disease in which abnormal cells grow uncontrollably and can spread to other parts of the body. It can affect almost any organ or tissue.
What are the most common types of cancer?
The most common types of cancer worldwide include:
- Breast cancer
- Lung cancer
- Prostate cancer
- Colorectal (colon) cancer
- Skin cancer
What are the main causes of cancer?
Cancer is caused by a combination of genetic, lifestyle, environmental, and infection-related factors, including:
- Smoking and alcohol
- Obesity and poor diet
- Exposure to chemicals or radiation
- Viral infections such as HPV or Hepatitis B/C
- Inherited gene mutations
What are the early symptoms of cancer?
Early cancer symptoms may include:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Persistent fatigue
- Lumps or swelling
- Changes in skin or moles
- Chronic pain
- Changes in bowel or bladder habits
How is cancer diagnosed?
Cancer is diagnosed through:
- Physical examination
- Imaging tests (X-ray, CT scan, MRI, ultrasound)
- Laboratory tests (blood and urine tests)
- Biopsy (gold standard)
- Genetic and molecular testing
Conclusion:
Cancer is a complex disease influenced by genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors.
Awareness of cancer causes, symptoms, types, diagnosis, treatment, complications, and prevention is essential for early detection and effective management.
Early recognition of cancer symptoms, participation in regular screening tests, and adoption of healthy lifestyle habits—such as maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, avoiding tobacco and alcohol, and protecting skin from UV exposure—can significantly reduce the risk of developing cancer.
Modern cancer treatments, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies, combined with supportive care, improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Understanding the complications of cancer and seeking timely medical intervention further enhances survival rates.

